Clients and parameters
To support the principle of interoperability any platform which can offer the input parameters in SAF or SMADSTEEL format can be a client for the service. The geometry must be defined as a collection of load transfer surfaces. To assign multiple pressure values to one load transfer surface a premeshing is required, which is practically a traditional finite element mesh of the surface always consisting planar faces. There are multiple choices regarding the type of finite faces of the mesh. Triangular meshes are flexible in terms of geometry (e.g., rounded, pitched-in corners) and always produce a regular mesh. Quadrilateral meshes are less flexible but tend to produce better results for load generation. Combined meshes try to combine the advantages of triangular and quadrilateral meshes. But in many cases, they produce an irregular mesh.
A simulation case starts from a set of parameters. The number of parameters can vary depending on the geometry and computational complexity, but even the simplest simulation requires a minimum of around 250 parameters which can be distinguished in four categories. Of course, a significant part of the parameters is redundant, so there is room for automation, which require a deliberate serialization process.
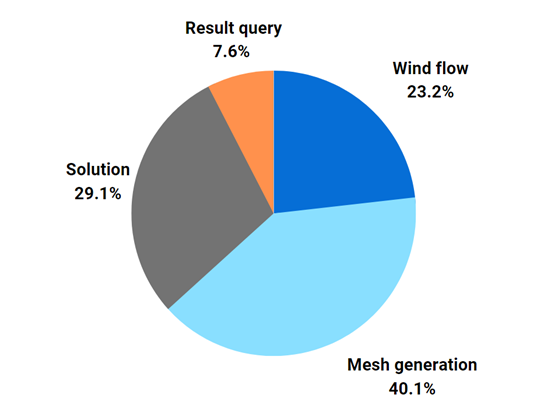
Distribution percentage of parameters
However, experience has shown that almost 80 % of the parameters can be fixed, for structural engineering purposes. This means that a default value is assigned. The necessary parameters are the following:
-
Wind flow
- Basic wind velocity according to EC
- Terrain category according to EC
- Wind direction vector
- Reference height – if it is not provided it is automatically calculated according to the top height of the building’s bounding box.
-
Mesh generation
-
Load transfer surfaces
-
Flag for premeshing - if the structure is considered premeshed or not.
-
Mesh type – the mesh face type if premesh is requested.
- Triangular
- Quadrilateral
- Combined
-
Load cell size – the desired face / cell size for load generation if premesh is requested.
-
Refinement – The refinement value according to the load cell size
-
Cell number between refinement levels
-
-
Solution
-
Turbulence model
-
Processor count for parallel computing
-
Iteration End
-
Convergence criteria
-
-
Result query
-
Load evaluation type
-
Mean
-
Maximum
-
Minimum
-
-
Load generation type
-
Node loads on vertices
-
Linear loads on beams
-
Uniform surface loads on faces
-
Linear surface loads on faces
-
Uniform surface loads on zones
-
Linear surface loads on zones
-
Uniform surface loads on specific zones
-
-
Zone interval for zone type load creation
-
Specific zones
-